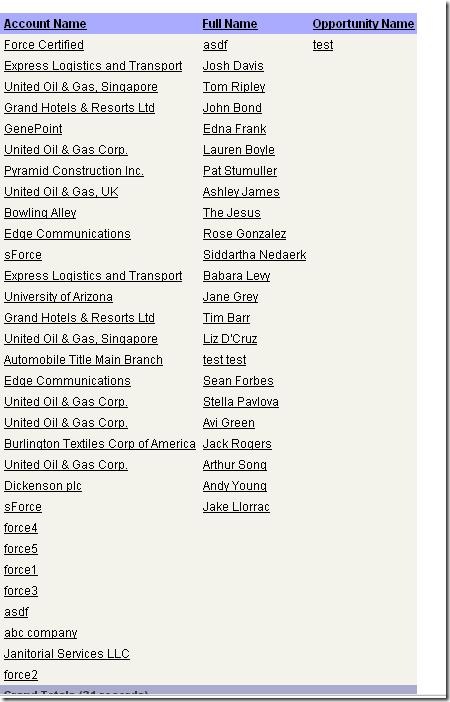
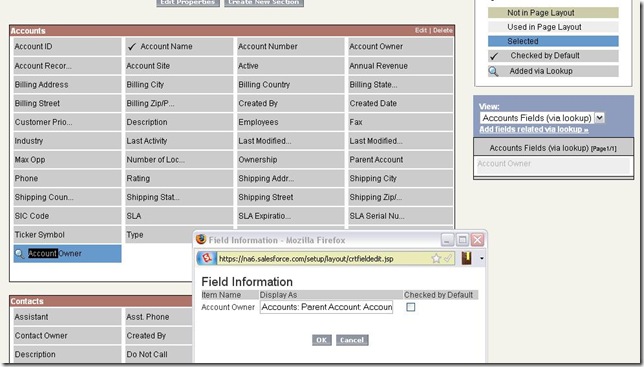
With this release, Salesforce certified folk are only required to complete training. No exam required!
I believe this training is open to the public. I was able to access it through this link, while logging in through one of my uncertified accounts.
The Sales Cloud
Analytic Enhancements
- Charts
- Greater control over labels and colors
- Donut and Funnel chart types added
- Not automatically enabled. When enabled, you cannot return to the old charting engine.
- Dashboards
- Analytic Snapshots
- Can now be bundled in managed and unmanaged packages
- Schedule and running user cannot be packaged and must be configured after package installation
Automated Campaigns
- Campaign Member
- View/edit/delete/clone each record
- Custom fields and page layout editor now available for campaign members (e.g. RSVP status, Food preference, etc.)
- Workflow rules for campaign members (e.g. if RVSP “Yes†send email alert with agenda)
- Use triggers for additional customization
- Setup –> Customize –> Campaigns –> Campaign Members
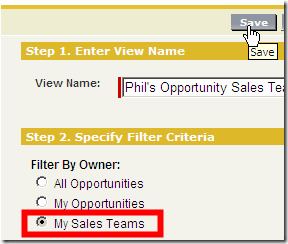
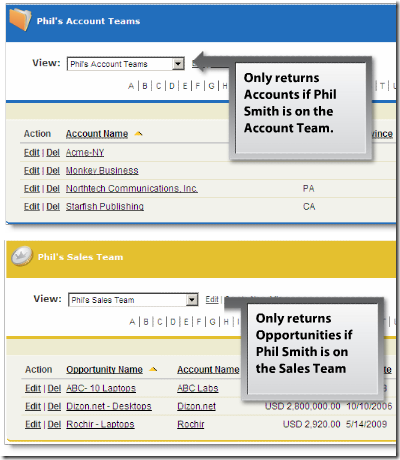
List Views for Account and Sales Teams
- My Sales Teams is now a filter criteria for list views on accounts and opportunities (account teams must be enabled)
Recurring Tasks
- Can edit individual tasks, or the series
- Must have an end date
- Provided button to calculate max end date (based upon number of tasks created)
- Recurrence icon on recurring tasks

- Turned on by default (but can be turned off)
- Outlook sync not supported for recurring tasks (planned for a future released)
Admin Enhancements
- Platform (Force.com Edition) profiles can now be given 10 existing CRM administrator permissions
- Delegated data administration now possible (View All and Modify All per object) on platform profiles
- Profile Setup Audit Trail logs changes to a profile, change author, and time of change
- When cloning a profile, Login Hours and Login IP Ranges are now cloned as well
Content Enhancements
- Content delivery now includes option for password protecting content
- Administrator can set default password (org wide) for content delivery
- Reporting for featured content and ratings
- Creation of content packs and the presentation assembly can now be disabled (org wide)
Mobile Enhancements
- Blackberry
- Related list now on the detail page of a record
- Clone existing records
- Create links from Salesforce records to visualforce pages or web tabs
- Improved Storm support
- iPhone
- List view enhancements
- Lead conversion support
- Calendar style browser for events
- Products and price book support
Sharing UI Enhancements
- Sharing administrator pages load faster
- Customized list views
The Service Cloud
Salesforce to Salesforce Cases and Case Comments
- Share records from one organization to another (Salesforce to Salesforce)
- Supports cases, leads, opportunities, accounts, contacts, activities, products, opportunity products, and custom objects
- Near real time updates
- Includes reporting and workflow capabilities
- Records can be shared manually or through sharing rules
Advanced Customer Portal User Management
- Ability to disable customer and partner users (new buttons on contact record)
- Ability to disable and an entire account’s access to customer and partner portals (new buttons on account record)
- Portal users can now be transferred between accounts (will take on role of new account or create a role will be created if none exists)
- Portal users can now be merged
Advanced Case Workflow
- Workflow rules can now be created when comments are added to cases
(notice that case is now selectable when creating a workflow rule on case comment)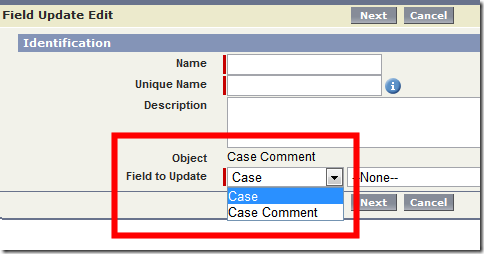
The Custom Cloud
Force.com Sites
- Publish VisualForce pages to branded domains entirely through the force.com platform.
- Sites is now live!
Organization-Wide Email Addresses
- Generic from email address and name
- Specify which profiles can send from each org wide address
- When sending an email, users select the email from the “from†address
- Can only be used when sending a single email (no mass email support, no workflow rules support!)
- Email address must be verified (activation link sent to address)
Workflow Process Visualizer
- Graphical representation of approval process (BETA)
- Read only representation
Visualforce Enhancements
- Ability to add visualforce page as a dashboard component
- Will display information based on the user logged in, not the running user
- Ability to use visualforce pages as custom help
(when users click this link)
Declarativ
e App Builder Enhancements
- TEXT() function support for picklists in formulas and workflow field updates
- INCLUDES(), ISNULL(), PRIORVALUE(), and ISCHANGED() support for multi-select picklists
- Support for encoding functions in formuals: HTMLENCODE, JSENCODE, JSINHTMLCODE, URLCODE
- Managed package versioning and deprecation support