Define a Case
From Salesforce:
A case is a detailed description of a customer’s feedback, problem, or question. Your organization can use cases to track and solve your customers’ issues. You can enter cases manually in the Cases tab, or your administrator can set up Web-to-Case and Email-to-Case to gather customer feedback from your company’s website and customer emails. Your customers can also create and submit new cases on your Self-Service portal.
Understand that cases are typically used for issue tracking and beyond that it really depends on your organization’s implementation.
Describe use cases for Case Hierarchies
Case hierarchies can be used to track sub-cases. For instance, let’s say that the IT department uses cases to log new user creations. In this situation, each new user requires 3 different accounts: salesforce.com, unix, and windows. HR must also prepare the person’s paperwork and have them sign off on this documentation. Here’s how this could break down using case hierarchy:
- Parent Case: New hire (person name), Case Owner: HR Person
- Child Case: Windows Login, Case Owner: Windows Admin
- Child Case: Unix Login, Case Owner; Unix Admin
- Child Case: Salesforce.com Login, Owner: SF Admin
Note that each case is owned by a different user (HR, Windows Admin, Unix Admin, SF Admin). This gives you much greater flexibility and accountability than having a single shared case.
Describe how to use Case Queues to manage Cases
Case queues work like any other queue. Unassigned cases should get assigned to a case queue until a user takes ownership of the issue. This is useful if you have a staff of different users resolving cases as they are available for work.
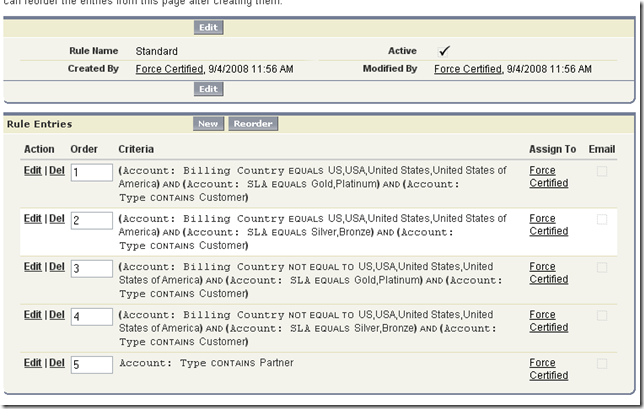
Describe how to use a Case Assignment Rule to assign and route Cases
Case assignment rules are similar to lead assignment rules. Rules are executed in order; if no order matches the default assignment is used.
Describe use cases for Web-to-Case
Customer request page on your company website. IT support request page on an intranet page. You can repurpose web-to-case for plenty of other processes as well.
Describe uses cases for Email-to-Case
An email address like support@salesforce.com. Basically the same principal applies to email-to-case as web to case: a support email account or helpdesk/call center situation is ideal for this. An added benefit of email-to-case is that incoming/outbound emails can be tracked and attached to cases automatically.
Note that email to case prior to Spring 09 required a software agent to be run behind the company firewall. Email to case on demand was released as a feature in the Spring 09 release and removes the need for this agent. Understand how each of these works and the differences between the two (essentially the agent monitors emails and assigns cases as needed, while on demand uses email forward to allow this process to happen on the Salesforce end).
Describe the functionality of the Case Escalation Rule
Case escalation rules are designed to escalate cases when they meet certain criteria. After X number of hours (and 30 minute increments). Case escalations can email up to 5 non Salesforce users.

Describe the functionality of the Case Auto-Response Rule
The case auto response rules can determine which email response will be sent when a customer submits a case through email, website, or self service portal. This allows you to configure different email responses for different customers, and so forth.
Describe the functionality of the Business Hours
Business hours allow you to assign cases to different time zones, and escalate cases according to time zone.
Example: East coast support staff and West coast support staff, both have business hours 8-5 and case to escalate after 3 hours. Each get a new case assigned at 4p EST. The East coast case will escalate the following day at 10a, while the West coast will escalate at 4p PST (7p EST). Without different business hours per time zone configured, they would both escalate at the same time.
Note that Age Over and Age are two different entities. Age (as defined in reporting) does not take business hours into consideration, while the escalation rules (Age_over) do use business hours. Last time I checked into this you could get a Business Age field added from Salesforce by request only.
Configure the settings and rules for Case processing, including Business Hours, and Escalation
- Customize –> Cases –> Support Settings
- Company Profile –> Business Hours
- Customize –> Cases –> Escalation Rules
- Default Case Owner
- Notify Default Case Owner
- Option to email case owner when a new case is assigned to them
- Automated Case User
- User listed in case history for default creation and actions until reassigned
- Case Creation Template
- Email to send to person requesting the case acknowledging creation of case
- Case Assigned Template
- Email to send to case owner
- Case Close Template
- Email sent to requestor indicating that the case is closed
- Email Case Comments Notification to Contacts
- When enabled allows contacts outside of the self service portal to receive notifications when case comments are updated
- Notify Case Owner of New Case Comments
- Early Triggers Enabled
- Enable Suggested Solutions
- Send Case Notifications from System Address
- If not checked, notification updates will be sent from user that updates the case
- Notify Case Owners when Case Ownership Changes
See “Customizing Support Settings†for more info.
Rules and the use of Email Templates
Customize –> Cases –> Auto-Response Rules
Case auto-response rules work the same as lead auto-response rules. The first rule met sends the associated email template and ends the process. If no rule is met, the default email template is used.
Define Solutions and how they can be associated with Cases
- A solution is a defined answer to a support issue. For instance, the solution “turn on computer†could be the answer to the case “cannot turn on computerâ€.
- Solutions have a many-to-many relationship to cases (a solution can be tied to many cases, and a case can have many solutions).
- See “How are Cases and Solutions related†for more info.
- Solutions have a status field (draft, published, etc) that allow for easy maintenance and prevent premature visibility of unapproved solutions. </L
i>
- Solutions can be made available in the self service portal and public knowledge base.
See “How are Cases and Solutions related†for more info.
Build a Solution Category tree and assign Solutions to Categories
Customize –> Solutions –> Solution Categories
Solutions are assigned in the categories related list in on the solution record. A solution can belong to many categories.
Define suggested solutions and explain where to use them
Suggested solutions are the top 10 recommended solutions based upon a hidden formula that rates based upon:
- Word frequency in all solutions
- Word frequency in similar cases with related solutions
- Proximity of the keywords within the solutions
- Word similarities to self-closed cases and solutions rated useful by Self-Service users
Suggested solutions can be used:
- Case page: click view suggested solutions and it will show the user entering the case.
- Customer Portal and Self Service Portal: Customers can view suggested solutions when they submit a case online.
- Case auto responses: you can add the merge field {!Case_Suggested_Solutions} and it will include these in the email.
Describe what content is accessible via the Self-Service Portal
Enterprise and Unlimited Edition only.
Cases can be logged; past cases can be viewed. Solutions can be browsed if this option is enabled. Suggested solutions can be enabled. Activities can be shown if marked as available for self service portal, as can case comments if the comment is marked publicly viewable.
Describe the ways to access the Self-Service Portal
The self service portal is accessed by users through a website; this site is generated when the self service portal is enabled by the system administrator. The system administrator can export the code or URL to the site and import this code/URL to the appropriate website.

Build a Case Queue, Assignment Rule, Web-to-Case, and corresponding Auto-Response Rule
- Manage Users –> Queues
- Customize –> Cases –> Assignment Rules
- Customize –> Self Service –> Web-to-Case (Pro+)
- Customize –> Cases –> Auto-Response Rules